Although the Conception Vessel is well known, it is of great importance to begin by understanding what this main channel itself represents. When we know the meaning of the vessel, our grasp of each point becomes deeper and more precise. For instance, Ren Mai is not simply a line across the body: it is the Sea of Yin itself — a current of nourishment, receptivity, and creation.
When we know the essence of the channel, the meaning of each point deepens: its qualities are not random but shaped by the vessel it belongs to.
Ren Mai is Yin, every point along its course is touched by Yin’s color, even when certain points lean toward Yang expression. It is as if the whole river dyes each stone it carries with its waters
This underlying nature colors, unifies the pathway, allowing us to appreciate each point not only in isolation but as part of a larger current of meaning
任脈 (Rèn Mài) — The Conception Vessel
任 (Rèn): The character 任 signifies "to bear, to carry responsibility, to entrust." It combines the person radical (亻) with the phonetic 壬, symbolizing the body's duty to nourish and sustain. In the Conception Vessel, it evokes the profound task of carrying life, whether in the womb, in the blood, or in the hidden spark of ideas yet to be born.
脈 (Mài): The character 脈 means "vessel, meridian, pulse." It combines 月 (flesh) with 永 (eternal flow), representing circulation that never ceases, the endless river of life within us.
Together —
任脈 (Rèn Mài): The Conception Vessel is called the "Sea of Yin," the channel that governs fertility, creation, and nourishment. More than a pathway, it is a living metaphor for the body's capacity to hold, sustain, and bring forth new beginnings.
Spiritual Symbolism: The Ren Mai embodies Yin — receptive, grounding, life-giving. It stabilizes Yang by containing it and is most influential in reproduction and childbirth. It is the vessel of beginnings, carrying the possibility of renewal in every cycle.
CV4 Guanyuan — 關元 (Gate of Origin)
Name & Imagery
CV4, Guanyuan — "Gate of Origin," stands as a luminous anchor of vitality on the Conception Vessel. This point evokes a sacred reservoir where Yin essence gathers and nourishes life. Often regarded as the body's energetic “wellspring,” Guanyuan is both a stabilizer and a source of creation, linking the lower abdomen to the depth of generative power.
Location
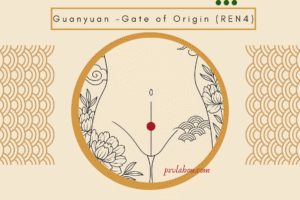
CV4 is located on the anterior midline of the lower abdomen, 3 cun below the umbilicus, and approximately 2 cun above the pubic symphysis. This placement situates it at the intersection of the body's energy and its creative potential, marking the threshold where essence consolidates and life force is fortified.

Classical Functions
In classical Chinese medicine, CV4 is prized for its role in strengthening Kidney and reproductive functions. It is used to tonify Qi and Yin, support fertility, regulate menstruation, alleviate urinary disorders, and enhance overall vitality. Daoist physicians referred to it as the "Origin of Vitality," a point to preserve essence, nourish life, and prolong longevity.
In short:
- Fortifies the original qi and benefits essence
- Tonifies and nourishes the Kidneys
- Warms and fortifies the Spleen
- Benefits the uterus and assists conception
- Regulates the lower jiao and benefits the Bladder
- Regulates Small Intestine qi
- Restores collapse
Guan Yan is a meeting point: it is the Front-Mu* point of the Small Intestine and also a central meeting point of the Conception vessel with the Spleen, Liver and Kidney channels
Modern Context
Today, CV4 is widely applied in acupuncture, moxibustion, and gentle acupressure to support reproductive health, improve pelvic floor function, and boost vitality. Its influence extends to both male and female reproductive systems and is considered a central point for holistic wellness, emotional grounding, and energetic balance.
 Symbolism and Cross-Cultural Echoes
Symbolism and Cross-Cultural Echoes
CV4 corresponds to the Svadhisthana (sacral) chakra in Indian traditions, emphasizing creativity, sexuality, and vitality. Both systems recognize the area as a core reservoir of life energy. Daoist texts depict CV4 as a hidden well or treasure, a sacred container of Yin essence whose careful preservation sustains longevity and vigor.
Point Combinations
CV4 is often paired with CV6 (Qihai) to strengthen Qi and consolidate the body’s lower energy. It may also be combined with CV3 (Zhongji) to regulate the lower jiao and reproductive organs, or with BL23 (Shenshu) to nourish the Kidneys, creating a network of points that harmonizes root and source.
Gentle Practice for Self-Care
To honor CV4, one can sit quietly with the breath sinking into the lower abdomen, visualizing the accumulation and circulation of life force. Gentle abdominal massage, moxibustion, or mindful pelvic awareness helps awaken grounding, vitality, and creative energy. Daily attention to this center nurtures both body and spirit.
Reflection
What sources of vitality do I carry within me, and how can I nurture them with care? Where in my life do I need to protect, replenish, and allow creation to flow freely?
*Cùn (寸) — The Body’s Inch
In acupuncture, a cùn is a traditional unit of proportional measurement, often translated as a “body inch.” Unlike a fixed ruler’s inch or centimeter, the cùn is relative to the patient’s own body, ensuring that point locations are tailored to each individual’s proportions. For example, the width of a person’s thumb at the knuckle is taken as 1 cùn, while the width of the four fingers held together equals 3 cùn. This system reflects Chinese medicine’s philosophy that the map of the channels should always be measured against the unique landscape of the body it belongs to.
*Lower Jiao in Classical Chinese Medicine
The body is traditionally divided into three jiaos (burners or energizers): the upper, middle, and lower jiao. These are not physical organs but functional regions describing how Qi, fluids, and essence move and transform.
Upper Jiao (胸, chest): compared to a mist, it governs respiration and the distribution of fluids.
Middle Jiao (腹, abdomen): compared to a bubbling cauldron, it governs digestion and the transformation of food into Qi and Blood.
Lower Jiao (下焦, pelvis): compared to a drainage ditch, it governs elimination, reproduction, and the storage of essence (jing).
The lower jiao includes the Kidneys, Bladder, Intestines, and reproductive organs. It is the seat of Yin, essence, and foundational vitality. Its healthy function ensures proper urination, bowel movement, menstruation, fertility, and sexual health.
*Front-Mu points (募穴, mù xué) are special acupuncture points located on the chest and abdomen. Each one corresponds to a specific internal organ (Zang-Fu).
“Mu” (募) means to gather or to collect.
These points are where the Qi of the organ gathers on the front of the body.
They are often used for diagnosis (they can be tender if the organ is imbalanced) and for treatment, especially of acute or excess conditions of the organ.
References
GB/T 12346-2021. Nomenclature and Location of Acupoints. Standardization Administration of China.
Huangdi Neijing (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Classic). c. 2nd century BCE.
Wiseman, N., & Ellis, A. Fundamentals of Chinese Medicine. Paradigm Publications, 1995.
Kaptchuk, T. J. The Web That Has No Weaver: Understanding Chinese Medicine. McGraw-Hill, 2000.
Panagiota Sophia Vlahou
Certified Beekeeper | Specializing in Traditional Beekeeping & Natural Wellness Methods
Trained in Traditional Acupuncture – Academy of Traditional & Chinese Medicine
Member of the Beekeepers’ Association of Attica-Greece
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease, and it does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet, lifestyle, or health practices.



